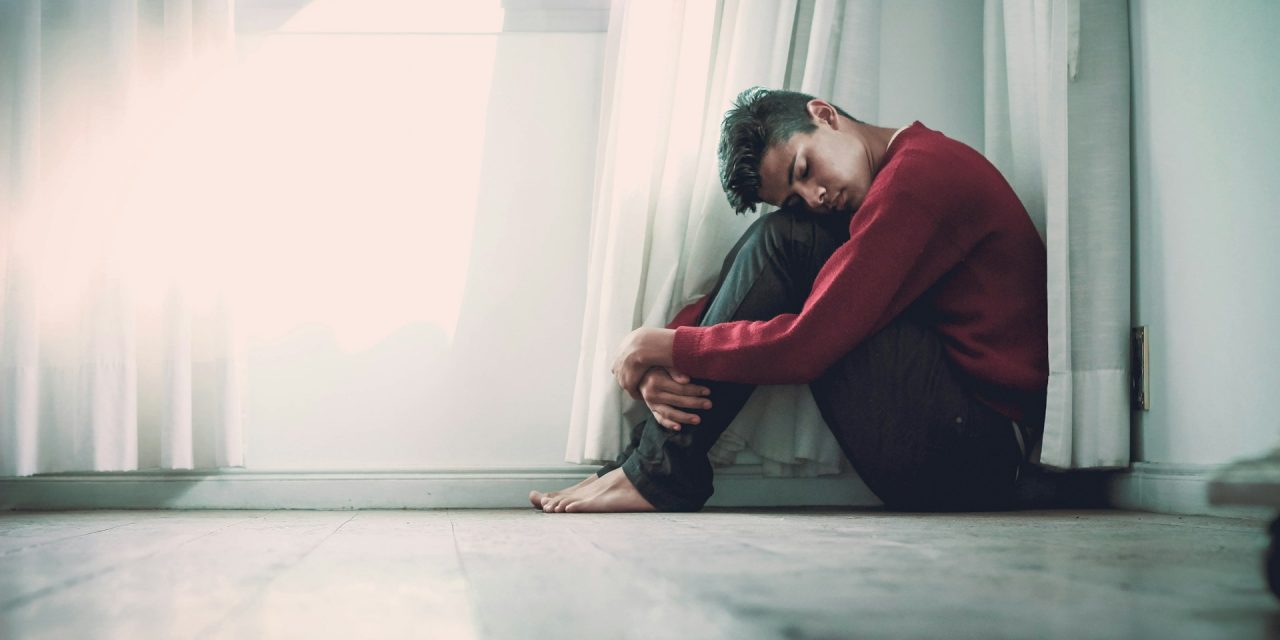
Wondering whether diabetes impacts your mental health? In this article, we explore the affects from diabetes on your well-being and health.
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. Type 1 diabetes involves the immune system mistakenly attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, while type 2 diabetes typically develops due to insulin resistance, where cells fail to respond to insulin effectively. Both types of diabetes require careful management to maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
The chronic stress of managing diabetes, including the constant vigilance required to monitor blood sugar levels, adhere to medication regimens, and maintain a healthy lifestyle, can significantly impact mental well-being. The fear of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, concerns about long-term complications, and the emotional burden of coping with a chronic illness can contribute to feelings of overwhelm, stress, and anxiety. The unpredictability of diabetes and the need for strict adherence to treatment plans can exacerbate feelings of anxiety and apprehension about the future. Conversely, mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety can complicate diabetes management by affecting adherence to treatment regimens, contributing to poor self-care practices, and impairing decision-making abilities. Recognizing and addressing the interconnectedness of mental health and diabetes is essential for providing comprehensive care and improving overall well-being for individuals living with these conditions.
Diabetes and Depression
Diabetes can induce depression in various interconnected ways. Firstly, the chronic stress associated with managing diabetes, including the daily demands of monitoring blood sugar levels, adhering to medication regimens, and making lifestyle adjustments, can take a toll on an individual’s mental well-being. The relentless nature of these tasks can lead to feelings of overwhelm, frustration, and helplessness, all of which are common triggers for depression. The fear of complications stemming from diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy, can contribute to a sense of hopelessness and pessimism about the future, further exacerbating depressive symptoms. The biochemical changes associated with diabetes, such as fluctuations in blood sugar levels and insulin resistance, can directly impact brain chemistry and neurotransmitter function, increasing susceptibility to depression.
Stigma surrounding the condition, feelings of isolation, and concerns about body image can all contribute to feelings of anxiety and self-doubt. Managing diabetes in social settings or dealing with unsupportive environments can further exacerbate feelings of anxiety and distress. can further contribute to the development or exacerbation of depression in individuals with diabetes. Overall, the complex relationship between biological, psychological, and social factors underscores the need for a holistic approach to managing both diabetes and depression in affected individuals.
How Diabetic Depression Affects the Everyday Life
Diabetic depression can have profound effects on the lives of individuals, impacting various aspects of their physical, emotional, and social well-being. Depression can significantly impair an individual’s ability to effectively manage their diabetes. The lack of motivation, energy, and interest that often accompanies depression can lead to neglect of self-care tasks such as monitoring blood sugar levels, adhering to medication regimens, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Consequently, this neglect can result in poorly controlled blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of diabetes-related complications and worsening overall health outcomes.
Diabetic depression can compound the symptoms and progression of diabetes-related complications. Depression has been associated with increased inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, both of which can contribute to the development and progression of complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, retinopathy, and kidney disease. Additionally, depression can impair immune function, making individuals more susceptible to infections and delaying wound healing, further exacerbating diabetes-related complications.
Beyond its physical impact, diabetic depression can also significantly affect an individual’s emotional and social functioning. Depression can lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and despair, making it difficult for individuals to find joy in their daily lives or engage in meaningful activities. Social withdrawal and isolation are common symptoms of depression, further exacerbating feelings of loneliness and disconnection from others. Depression can strain relationships with family members, friends, and caregivers, leading to increased feelings of isolation and loneliness. Diabetic depression can impact an individual’s overall quality of life and well-being. The chronic stress of living with both diabetes and depression can take a toll on an individual’s mental and emotional resilience, leading to decreased overall satisfaction with life. Depression can also contribute to feelings of worthlessness and self-doubt, making it challenging for individuals to envision a positive future or set and achieve meaningful goals.
Way Towards Mental Well-being
Coping with diabetic depression is possible through a combination of self-care strategies, professional support, and lifestyle modifications:
Support from Network
Individuals can benefit from building a strong support network consisting of family members, friends, and healthcare professionals who can offer understanding, encouragement, and practical assistance. Engaging in regular social activities, participating in support groups, and connecting with others who share similar experiences can help combat feelings of isolation and loneliness often associated with depression.
Stress Management
Practicing stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help individuals reduce feelings of anxiety and overwhelm. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, has been shown to improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression by releasing endorphins, the body’s natural mood boosters.
Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by following a balanced diet including sugar-free diet, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can help support overall mental and emotional well-being. Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adhering to medication regimens as prescribed by healthcare providers are essential components of managing both diabetes and depression.
Professional Help
Seeking professional help from mental health professionals, such as therapists, counselors, or psychiatrists, can provide individuals with the tools and resources needed to effectively manage their depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), a type of talk therapy, has been shown to be particularly effective in treating depression by helping individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of depression. Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), can help alleviate symptoms of depression by restoring chemical imbalances in the brain. It’s essential for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the most effective treatment approach for their specific needs.
Finally, maintaining a positive outlook and setting realistic goals for self-care and recovery are crucial aspects of coping with diabetic depression. Celebrating small victories, practicing self-compassion, and focusing on what is within one’s control can help individuals maintain hope and resilience in the face of adversity.
Timely Intervention and Management
Depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric disorders are common among individuals with diabetes, affecting their quality of life, self-care behaviors, and overall health outcomes. However, with comprehensive support, effective management strategies, and timely intervention, individuals can better cope with the challenges of living with diabetes and improve their mental and emotional well-being. By integrating mental health care into diabetes management plans and promoting holistic approaches to self-care, healthcare providers can help individuals lead fulfilling lives and achieve better health outcomes. By adopting a holistic approach to self-care and seeking appropriate support and treatment, individuals can effectively cope with diabetic depression and improve their overall quality of life.